The Diamond Structure
Diamond structure
Point set for diamond structure
0.00 0.00 0.00
0.50 0.50 0.00
1.00 1.00 0.00
0.25 0.25 0.25
0.75 0.75 0.25
0.50 0.00 0.50
1.00 0.50 0.50
0.50 1.00 0.50
0.00 0.50 0.50
0.75 0.25 0.75
0.25 0.75 0.75
1.00 0.00 1.00
0.50 0.50 1.00
0.00 1.00 1.00
The path
Path1: 1,4,2,5,3
Path2: 5,8,11,9,4,6,10,7,5
Path3: 14,11,13,10,12
conn1: 3,5
conn2: 5,14
diamond_Points for one diamond unit
Each diamond unit has 14 vertexes, of which 4 (4#, 5#, 10#, 11# in Table 1) are inside the cube, 6 (2#, 6#, 7#, 8#, 9#, 13#) are onto each surface of the cube, and the remaining 4 (1#, 3#, 12#, 14#) are at the vertexes of the cube (Fig 1).
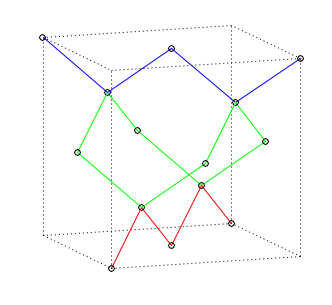
Fig 1. One diamond unit
Table 1. Point-set for one diamond unit with $a=1$.
0.00 0.00 0.00
0.50 0.50 0.00
1.00 1.00 0.00
0.25 0.25 0.25
0.75 0.75 0.25
0.50 0.00 0.50
1.00 0.50 0.50
0.50 1.00 0.50
0.00 0.50 0.50
0.75 0.25 0.75
0.25 0.75 0.75
1.00 0.00 1.00
0.50 0.50 1.00
0.00 1.00 1.00
Degree of unsaturation (U) of the vertexes
As in Fig 1, there are three types of vertexes in each diamond unit - inside points, face points, and vertex points (Table 2). So the number of effective points of one diamond unit is
$$ 14-24/4=8 $$
.
| U | $z$ value | Num of Points | |
|---|---|---|---|
| inside points | 0 | $a/4$, $3a/4$ | 4 |
| face points | 2 | $0$, $a/2$, $a$ | 6 |
| vertex points | 3 | $0$, $a$ | 4 |
| sum | 24 | 14 |
3 Types of Operations
T1
Translate the diamond unit with one unit $a$ along one of the axes ($x$, $y$, and $z$). There are 6 equvalent T1 translation operations in total.
| $x$ | $y$ | $z$ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| $T1_{\pm x}$ | $\pm 1$ | $0$ | $0$ |
| $T1_{\pm y}$ | $0$ | $\pm 1$ | $0$ |
| $T1_{\pm z}$ | $0$ | $0$ | $\pm 1$ |
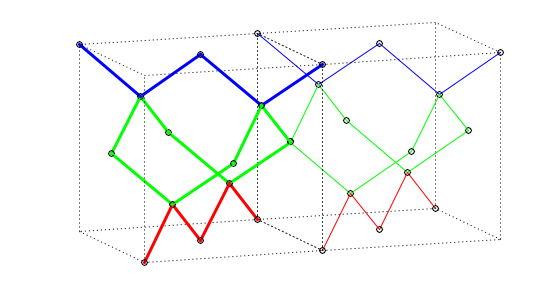
Fig 2. Example of T1 operation, $T1_{+x}$.
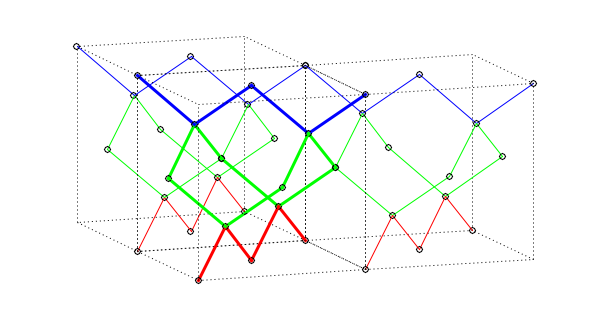
Fig 3. Example of two T1 operations, $T1_{+x, +y}$.
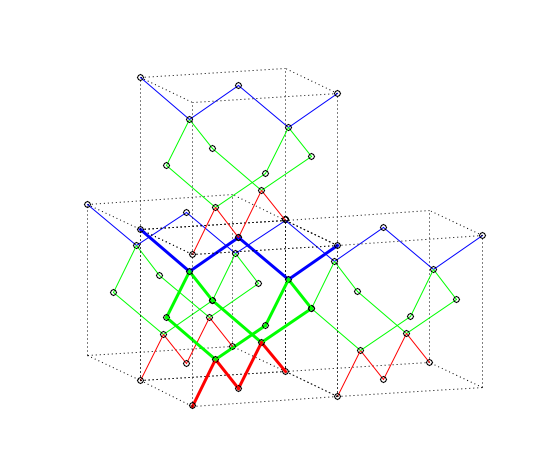
Fig 4. Example of three T1 operations, $T1_{+x, +y, +z}$.
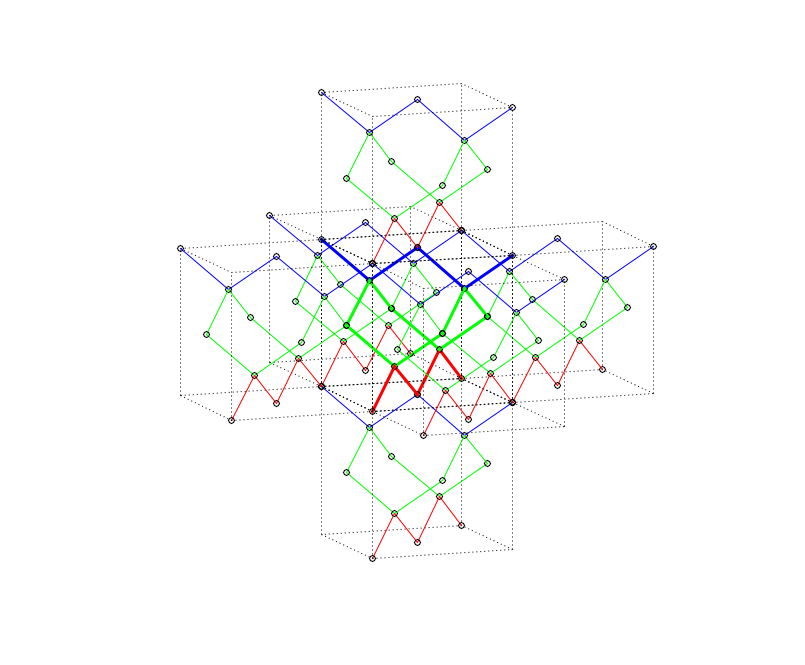
Fig 5. All T1 operations.
T2
Translate the diamond unit with two steps - each step is $a$ along one of the axes and the two steps are in different axes. There are 12 equvalent T2 translation operation in total.
| $x$ | $y$ | $z$ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| $T2_{\pm x\pm y}$ | $\pm 1$ | $\pm 1$ | $0$ |
| $T2_{\pm y\pm z}$ | $0$ | $\pm 1$ | $\pm 1$ |
| $T2_{\pm x\pm z}$ | $\pm 1$ | $0$ | $\pm 1$ |
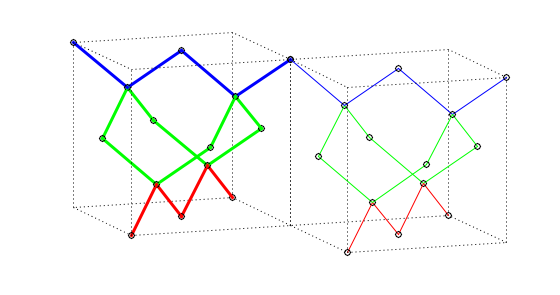
Fig 6. Example of T2 operation, $T2_{+x-y}$.
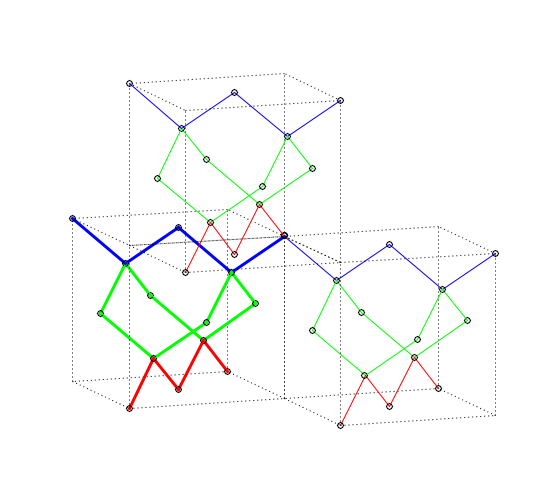
Fig 7. Example of two T2 operations, $T2_{+x-y, -y+z}$.
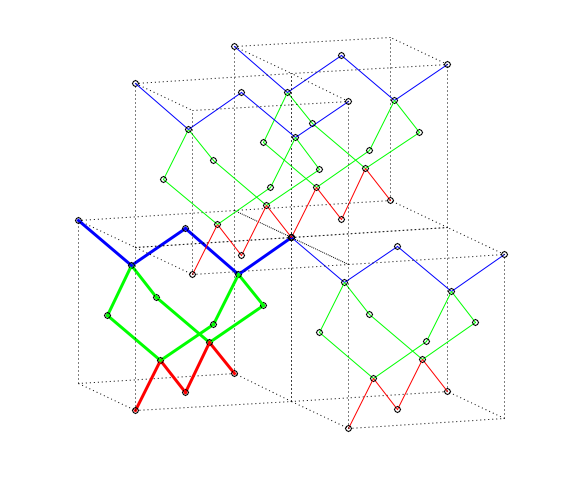
Fig 8. Example of three T2 operations, $T2_{+x-y, -y+z, +x+z}$.
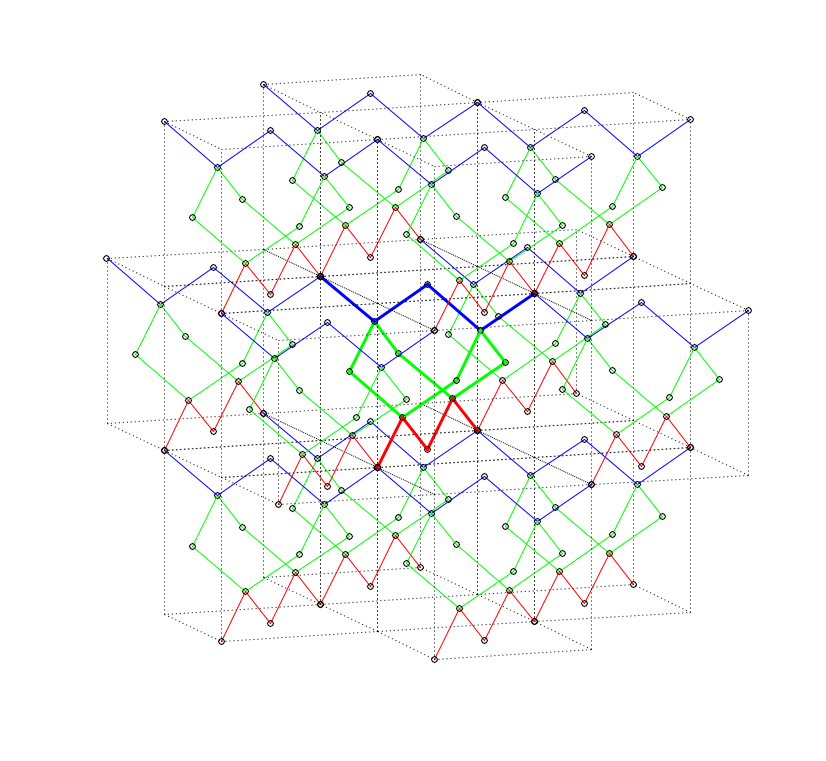
Fig 9. All T2 operations.
T3
Translate the diamond unit with three steps - each step is $a$ along one of the axes and these steps are in different axes. There are 8 equvalent T3 translation operation in total.
| $x$ | $y$ | $z$ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| $T3_{\pm x\pm y\pm z}$ | $\pm 1$ | $\pm 1$ | $\pm 1$ |
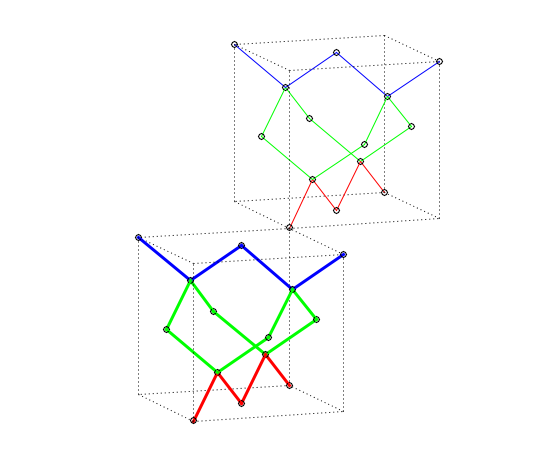
Fig 10. Example of T3 operation, $T3_{+x+y+z}$.
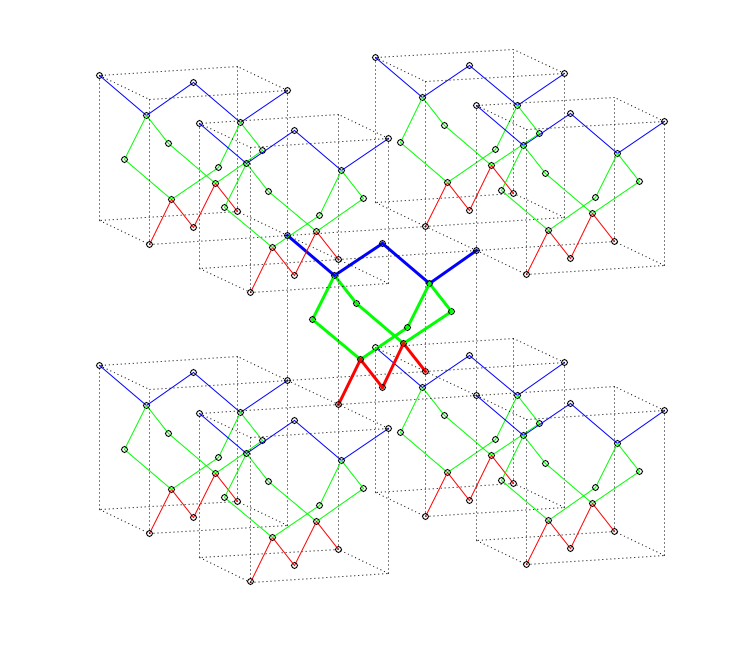
Fig 11. All T3 operations.
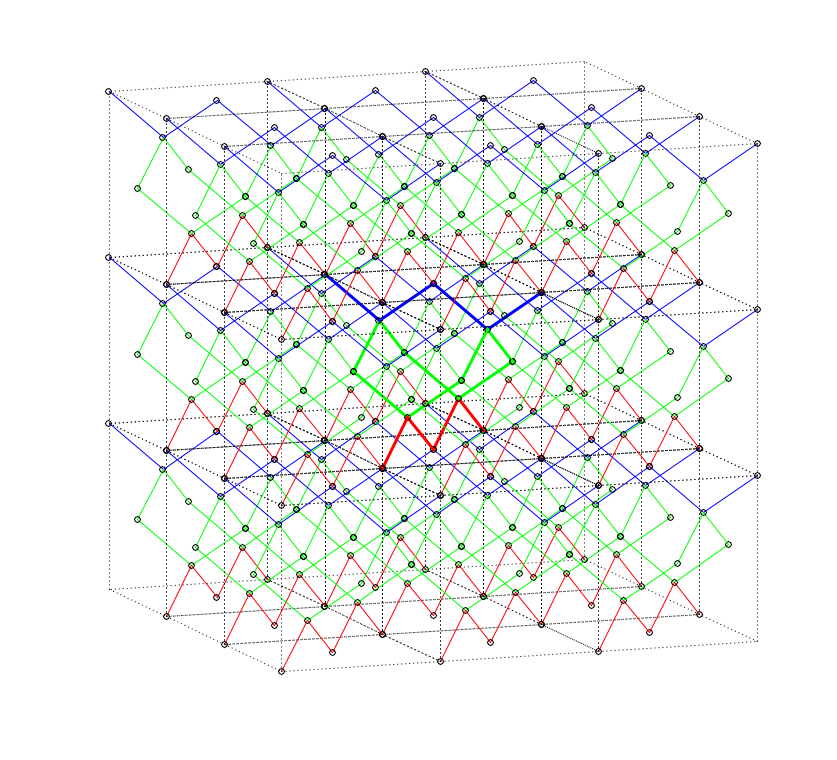
Fig 12. All T1, T2, and T3 operations.